Statistical Data on Drugs in Louisiana
Based on the compiled data from various reports and surveys, Louisiana faces significant challenges with drug use, addiction, and overdose deaths. The state consistently ranks above national averages in several key metrics related to substance abuse and has seen concerning trends in recent years, particularly with opioids and fentanyl.
Drug Overdose Statistics
- 2021: 55.9 deaths per 100,000 (above U.S. average)
- 2022: 54.5 deaths per 100,000 (36.71% above national average)
- Total deaths in 2022: 2,376
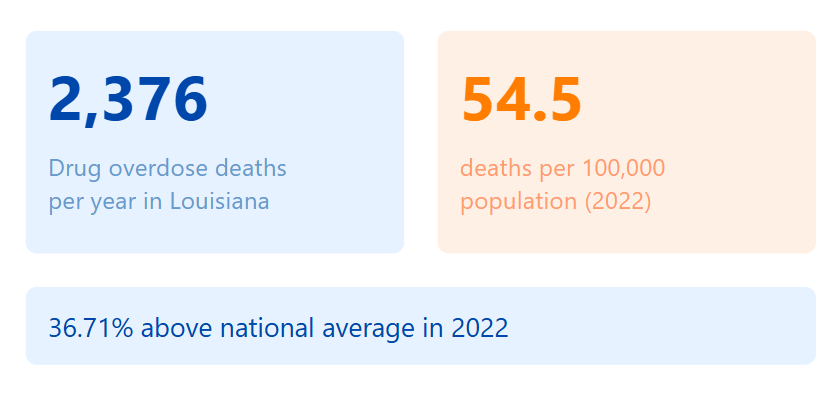
The data shows a persistent increase in overdose deaths, with Louisiana consistently maintaining rates above the national average. This indicates a serious public health crisis requiring immediate attention.
Opioid-Specific Death Statistics
| Year | Deaths | Rate per 100,000 |
| 2015 | 287 | 6.3 |
| 2016 | 346 | 7.7 |
| 2017 | 415 | 9.3 |
| 2019 | 444 | 9.9 |
| 2021 | 1,335 | 30.5 |
Opioid deaths show a dramatic increase from 2015 to 2021, with a particularly sharp rise between 2019 and 2021, indicating an escalating crisis.
Fentanyl Death Trends
| Year | % Change in Deaths |
| 2016 | +150% |
| 2017 | +80% |
| 2021 | 91% of all overdose deaths |
Fentanyl-related deaths show dramatic increases, becoming the dominant factor in overdose fatalities.
County-Level Data
Washington County:
- Highest death rate: 57.5 per 100,000
- Funding per capita: $3.04 (2017) to $3.35 (2018)
Orleans Parish: 97 deaths per 100,000
Calcasieu Parish (2022):
- Total overdoses: 64
- Fentanyl-related: 52 (81%)
Significant disparities exist in overdose rates across counties, with some areas showing extremely high death rates despite receiving minimal per-capita funding.
Historical Trends
Drug poisoning death records:
- 2014: 53.1% unspecified drug codes
- 2021: 35.2% unspecified drug codes
- 2014: 32% opioid involvement
- 2021: 53.4% opioid involvement
The data shows improved specificity in death reporting over time, while revealing a significant increase in opioid involvement in fatalities.
General Substance Use Statistics (2021)
| Category | Total Count |
| Illicit Drug Users | 550,000 |
| Marijuana Users (Past Year) | 727,000 |
| Pain Reliever Misuse | 143,000 |
| Cocaine Use (Past Year) | 66,000 |
| Methamphetamine Use | 49,000 |
| Total Substance Use Disorder | 698,000 |
Louisiana faces a substantial substance use challenge, with nearly 700,000 individuals affected by substance use disorders. Marijuana remains the most widely used substance, while the concerning numbers for pain reliever misuse reflect the state’s ongoing opioid crisis.
Substance Use by Age Group (2021)
| Age Group | Drug Use Disorder | Opioid Use Disorder |
| 12–17 | 9.18% | 1.10% |
| 18–25 | 17.66% | 1.44% |
| 26+ | 9.40% | 3.46% |
Young adults (18-25) show the highest rates of drug use disorder, while opioid use disorder is most prevalent among adults over 26.
Regional Comparison (2017-2019)
| Category | Louisiana | Regional Avg | National Avg |
| Marijuana Use (12–17) | 4.1% | 5.6% | 6.8% |
| Illicit Drug Use (12–17) | 5.8% | 7.0% | 8.2% |
| Young Adult Marijuana Use | 28.6% | 27.5% | 35.0% |
Louisiana’s lower rates of youth substance use compared to regional and national averages suggest some success in prevention efforts for younger populations. However, this relative success contrasts with the state’s high overdose death rates and prescription rates, indicating different challenges across age groups and substances.
Youth Drug Use (Ages 12-17)
- Illicit drug use: 6.35% (23,000 youth)
- Marijuana use: 78.26% of drug users
- Pain reliever misuse: 2.49%
- Cocaine use: 0.28%
- Methamphetamine use: 0.28%
- Heroin use: 0.14%
Youth drug use in Louisiana is 23.76% lower than the national average, suggesting relatively effective prevention programs for this age group.
School-Related Drug Statistics
Gender breakdown: males: 30% offered/sold drugs at school; females: 21% offered/sold drugs at school
Grade level exposure:
- 9th-10th: 26%
- 11th: 24%
- 12th: 22%
Drug exposure in schools shows consistent gender disparity and slightly decreases with grade level.
High School Drug Use (2011 Survey)
Marijuana statistics:
- Lifetime use: 34% (vs. 40% national)
- Recent use (past 30 days): 17% (vs. 23% national)
- School property use: 4% (vs. 6% national)
Gender differences:
- Males: Higher rates across all categories
- Lifetime use: Males 40% vs. Females 29%
- Recent use: Males 20% vs. Females 14%
Louisiana high school students generally show lower drug use rates compared to national averages, with consistent gender disparities showing higher use among males.
Prescription Pain Reliever Statistics (2015-2017)
| Year Range | Misuse Rate | Heroin Use Rate |
| 2015–2016 | 4.57% | 0.22% |
| 2016–2017 | 4.12% | 0.22% |
While pain reliever misuse showed slight decline, heroin use remained stable, suggesting possible shifts in drug use patterns.
Prescription Statistics
- Current rate: 74.4 prescriptions per 100 persons
- National average: 43.3 prescriptions per 100 persons
- Decrease from 113.7 (2008) to 89.5 (2017)
Despite a significant 21% decrease in prescription rates, Louisiana still maintains a prescription rate 72% higher than the national average, suggesting continued overprescription issues.
Drug Use Impact (Recent Data)
- HIV/AIDS cases from IV drug use: 20,424
- Hepatitis C cases from IV drug use: 50,000
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal: 0.56% of births
- Naloxone prescriptions: 159.8 per 100,000 persons (vs. 182.8 national average)
The health impact of IV drug use in Louisiana is severe, with over 70,000 combined cases of HIV/AIDS and Hepatitis C, while the lower-than-national-average rate of naloxone prescriptions suggests potential gaps in overdose prevention resources. The presence of neonatal Opioid Withdrawal in newborns further underscores the broad societal impact of the opioid crisis.
Treatment Statistics
- Active treatment facilities: 151
- Annual patients treated: 10,633
Treatment breakdown (2019):
- Drug problem only: 58.5%
- Alcohol problem only: 10.6%
- Both drug and alcohol: 30.9%
Treatment costs:
- Outpatient: Average $1,795 per person
- Residential: Average $56,822 per person
The limited number of treatment facilities (151) serving over 10,000 patients annually indicates a significant capacity challenge, especially given the high cost of residential treatment ($56,822) compared to outpatient care ($1,795). The fact that nearly 90% of patients seek treatment for drug-related issues (either alone or with alcohol) aligns with Louisiana’s documented drug crisis.
Treatment Need vs. Access (2021)
| Category | Total Need | Not Receiving Treatment |
| Illicit Drug Treatment | 316,000 | 289,000 (91.5%) |
| Substance Use Treatment | 607,000 | 573,000 (94.4%) |
A significant treatment gap exists, with over 90% of those needing treatment not receiving it.
Treatment Facility Statistics (2019)
- Medication-Assisted Treatment: methadone: 3,008 patients; buprenorphine: 1,673 patients
- Facilities offering free treatment: 6
- Annual outpatient enrollments: 9,008
- Annual residential enrollments: 1,297
- Hospital-based treatment: 328 patients
The data shows a significant reliance on medication-assisted treatment, with methadone being the more commonly used option. However, the limited number of facilities offering free treatment suggests potential access barriers for lower-income individuals.
Annual Admissions by Drug Type (2019)
- Marijuana: 6,022
- Cocaine: 3,798
- Prescription opioids: 3,324
- Heroin: 1,866
- Amphetamines: 1,229
The admission numbers reflect marijuana as the primary cause for treatment, followed by cocaine and prescription opioids. The relatively low number of facilities (151) compared to the number of people needing treatment suggests potential access issues.
Treatment Categories (2018)
- Treatment and recovery: 24%
- Prevention: 21%
- Mixed treatment/recovery/prevention: 36%
- Research: 1%
- Criminal justice: 13%
- Law enforcement: 6%
The distribution shows a balanced approach between treatment and prevention, though the low percentage allocated to research might limit innovation in addressing the crisis. The significant criminal justice component reflects the dual health/law enforcement nature of the challenge.
Treatment Costs and Funding
| Year | Total Funding | Per Capita |
| 2017 | $48,259,917 | $10 |
| 2018 | $82,567,684 | $18 |
The substantial increase in funding (71%) from 2017 to 2018 shows growing recognition of the crisis, though the per capita spending remains relatively low given the scale of the problem.
Medicaid Spending on Treatment
| Year | Buprenorphine | Naltrexone | Naloxone | Total |
| 2016 | $12,102,145 | $308,138 | $193,524 | $12,688,603 |
| 2017 | $21,568,180 | $1,109,879 | $129,498 | $22,861,767 |
| 2018 | $25,780,202 | $1,818,336 | $231,894 | $27,843,513 |
The steady increase in Medicaid spending, particularly on buprenorphine, indicates growing reliance on medication-assisted treatment. The rising naltrexone spending suggests diversification of treatment approaches.
Healthcare Impact
Opioid-related hospitalizations:
- 2013: 6,850 cases
- 2016: 13,300 cases
The near doubling of opioid-related hospitalizations over three years demonstrates the escalating burden on the healthcare system, though improved insurance coverage through Medicaid expansion has helped address access to care.
Louisiana’s drug statistics reveal a critical public health crisis with 2,376 overdose deaths in 2022, far exceeding national averages, while opioid deaths increased dramatically from 287 in 2015 to 1,335 in 2021. The treatment gap remains severe, with over 90% of those needing help unable to access it, despite having 151 facilities serving 10,000 patients annually.
Statistical Data on Alcohol in Louisiana
Louisiana faces significant challenges with alcohol consumption across different age groups and demographics. The state ranks above the national average in excessive drinking, with concerning trends in both urban and rural areas. The data shows particular challenges with underage drinking and a high rate of alcohol-related deaths.
General Alcohol Deaths and Impact
- Total annual deaths: 2,278
- Deaths under 21: 4.1% (113 deaths)
- Male deaths: 71.4%
- Adults 35+ deaths: 79.0%
- Years of potential life lost: 62,928
- Economic impact (2022 adjusted): $5.132 billion
- Cost per drink: $2.58
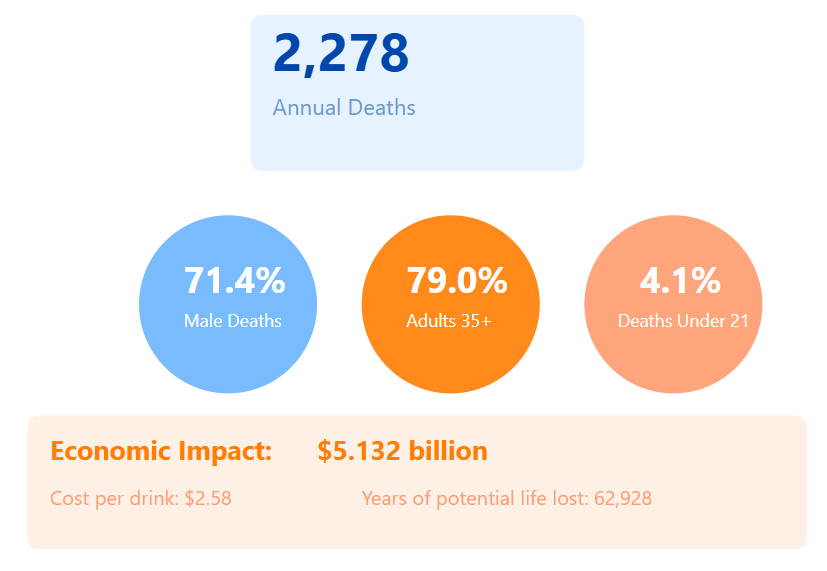
The economic and human cost of alcohol abuse in Louisiana is substantial, with males representing the majority of alcohol-related deaths and significant years of life lost.
Adult Drinking Patterns
- Adults who binge drink monthly: 18.1%
- Median drinks per binge: 5.5 drinks
- Top 25% heaviest drinkers: 7.4 drinks per binge
- Binge frequency: Median 2.0 times monthly
- Heavy drinkers (top 25%): 4.7 times per month
- Excessive drinking rate: 17.4% (ranks 31st nationally)
The data reveal a concerning pattern of heavy drinking among Louisiana adults, with a notable subset engaging in frequent and intense binge drinking episodes.
Age Group Breakdown (2021)
| Age Group | Past Month Use | Binge Drinking | Alcohol Use Disorder |
| 12–17 | 6.94% | 4.00% | 2.72% |
| 18–25 | 47.48% | 28.39% | 13.48% |
| 26+ | 48.10% | 25.25% | 10.96% |
Alcohol use increases dramatically from adolescence to young adulthood, with young adults showing the highest rates of both use and disorder.
Youth Statistics: High School Students
- Lifetime alcohol use: 76% (vs 71% national)
- Past 30-day use: 44% (vs 39% national)
- Heavy episodic drinking: 23%
- Drinking on school property: 6%
Grade-level Breakdown
- 9th-10th grade: 70% lifetime use
- 11th grade: 80% lifetime use
- 12th grade: 86% lifetime use
Louisiana’s youth drinking rates exceed national averages, with concerning progression in alcohol use through high school years. The data shows particular vulnerability during the transition between grades.
Demographic Analysis (2006 Data)
| Category | Binge Drinking | Heavy Drinking | Past Month Use |
| Male | 19.1% | 6.1% | 54.5% |
| Female | 7.7% | 3.3% | 38.3% |
| White | 15.2% | 5.2% | 51.1% |
| Black | 7.9% | 3.1% | 36.0% |
Significant disparities exist across gender and racial lines, with white males showing consistently higher rates of all types of alcohol use.
Highest Risk Groups
- Age: 18-34 years (19.2% binge drinking rate)
- Education: Some college/graduate (14.8%)
- Income: $50,000+ (18.0%)
- Employment: Employed (16.3%)
The data indicate that young, employed people with higher education and income levels are most likely to engage in risky drinking behaviors.
Parish-Level Data
- Lafourche Parish: 24% excessive drinking (highest in state)
- Livingston Parish: 23% excessive drinking
- State average: 22%
- National average: 19%
- Alcohol-impaired driving deaths (2021): 31% of crash deaths
Significant geographic variations exist in excessive drinking rates, with some parishes substantially exceeding both state and national averages.
Treatment Gap Statistics (2021 data, in thousands)
People needing but not receiving treatment for alcohol use: 398,000 total
- Ages 12-17: 10,000
- Ages 18-25: 60,000
- Ages 26+: 327,000
The data shows a severe treatment access problem, with the majority of the gap occurring in the adult population over 26. This suggests that while younger populations might have better access to treatment through school or family interventions, working adults face significant barriers to accessing care.
Louisiana’s alcohol statistics reveal a critical public health crisis, with 2,278 annual deaths, nearly 63,000 years of potential life lost, and a staggering $5.1 billion economic impact. The treatment gap is severe, with only 7.1% of those needing help receiving it, leaving over 398,000 individuals without necessary care. Young adults (18-25) and white employed males show the highest risk patterns, while the 76% lifetime alcohol use rate among high school students significantly exceeds national averages, indicating a pressing need for both enhanced prevention efforts and improved treatment accessibility.
In general, Louisiana faces a dual crisis of drug and alcohol abuse, with 2,376 drug overdose deaths and 2,278 alcohol-related deaths annually, creating a combined economic burden exceeding $5.1 billion. The treatment system is severely strained, with only 151 facilities serving over 10,000 patients annually, while more than 90% of those needing treatment for either substance cannot access it. Young adults (18-25) show the highest risk patterns for both substances, pointing to a critical need for expanded prevention and treatment services targeting this vulnerable age group.
Sources:
- Drug Abuse Statistics
- Mental Health and Substance Use State Fact Sheets: Louisiana | KFF
- LOUISIANA – National Survey on Drug Use and Health
- Addiction and Overdose Statistics in Louisiana
- Opioid Deaths in Louisiana
- Behavioral Health Barometer: Louisiana, Volume 6
- STATE CASE STUDIES Louisiana
- Alcohol and Drug Use Among Louisiana Public School Students
- Alcohol Use
- Louisiana has more than the U.S. average of adults who excessively drink. See national data.
- Explore Excessive Drinking in Louisiana | AHR
- Avenues Recovery Analyzes Louisiana’s Substance Abuse Statistics
- Addiction and Overdose Statistics in Louisiana
- Louisiana ranks among the highest in overdose death rates, according to CDC
- Map: These Louisiana parishes are home to the most excessive drinkers, study finds